The widespread DNS hijacking Roaming Mantis malware of routers that recently found the targeting of Android devices has been updated to target iOS devices and desktop users.
Nicknamed Mantis Roaming, malware was originally found hijacked by Internet routers last month to distribute Android banking malware designed to steal user login credentials and a secret code for two-factor authentication.
According to security researchers at Kaspersky Labs, the criminal group behind the Roaming Mantis malware has expanded its targets by adding phishing attacks to iOS devices and a cryptocurrency extraction script for PC users.
Moreover, while the initial attacks were aimed at Southeast Asian users, including South Korea, China, and Japan, the new campaign now supports 27 languages to expand its activities to people in Europe and the Middle East. -orient.
How Roaming Mantis malware works
Similar to the previous version, the new Roaming Mantis malware is distributed via DNS hijacking, where hackers change the DNS settings of wireless routers to redirect traffic to malicious sites controlled by them.
Therefore, whenever users try to access a website through a compromised router, they are redirected to malicious websites that offer:
fake applications infected by banking malware to Android users, phishing sites for iOS users,
Sites with cryptographic extraction scripts for desktop users
“Once the [Android] user is redirected to the malicious site, you are prompted to update the browser [app], resulting in a download of a malicious application called chrome.apk (there is another version, called Facebook. apk), the researchers say.
To avoid detection, fake websites generate new packages in real time with unique malicious Apk files to download and set the file name as eight random numbers.
Once installed, hackers can control infected Android devices using 19 built-in backdoor commands, including -sendSms, set wifi, gcont, lock, onRecordAction, call, get_apps, ping, and more.
Also Read: Top 10 Business Lessons From BILL MICHELON
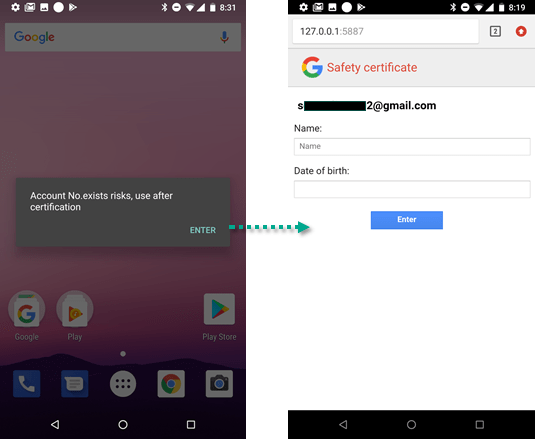
If victims have an iOS device, the malware redirects users to a phishing site that mimics the Apple website, claiming to be “security.app.com” and asks them to enter their user ID, password, number of paper, card expiration date and CVV number.
In addition to stealing sensitive information from Android and iOS devices, the researchers found that Roaming Mantis malware is injecting a browser-based cryptocurrency browser from CoinHive on each landing page if visited with Monero.
Bearing in mind these new capabilities and the rapid growth of the campaign, the researchers believe that “those who support it have a strong financial motivation and are probably well funded”.
Here’s how to protect yourself from the wandering Roaming Mantis malware
To protect against this malware, we recommend that you verify that the router is running the latest firmware and that it is protected by a secure password.
Because the hacking campaign uses attack-controlled DNS servers to fake legitimate domains and redirect users to malicious download files, it’s a good idea to make sure that the sites you visit are HTTPS-compliant.
It is also necessary to disable the remote administration functionality of the router and the hardware code of a reliable DNS server in the network settings of the operating system.
Users of Android devices are still encouraged to install apps from official stores and disable app installs from unknown sources on their smartphones by going to Settings → Security → Unknown sources.
To check if your Wi-Fi router is already compromised, check your DNS settings and check the DNS server address. If it does not match the one published by your provider, replace it with the coupon. Also, change all the passwords in your account immediately.



